Sanftes Scrollen für Anker-Links in Svelte mit TypeScript
In dieser Schritt-für-Schritt-Anleitung werden wir die smoothScrollTo-Funktion von Grund auf in Svelte und TypeScript erstellen, um eine sanfte Scroll-Animation in Ihrer Webanwendung zu ermöglichen.

Inhaltsverzeichnis
Schritt 1: Projektvorbereitung
Stelle sicher, dass Du ein Svelte-Projekt hast und TypeScript als Sprache verwendest. Falls Du noch kein Svelte-Projekt erstellt habst, kannst Du dies mit dem folgenden Befehl tun:
npx degit sveltejs/template svelte-app
cd svelte-appInstallieren Sie außerdem die Typen für TypeScript:
npm install --save-dev @tsconfig/svelte typescriptSchritt 2: Erstellen der smoothScrollTo-Funktion
Erstelle eine neue Datei namens smoothScrollTo.ts im Root-Verzeichnis Deines Projekts. Diese Datei wird unsere smoothScrollTo-Funktion enthalten.
export const smoothScrollTo = (scrollTargetID: string, menuElementID: string, topOffset: number) => {
// Wir füllen die Funktion in den nächsten Schritten...
};Schritt 3: DOM-Abfrage und Berechnung der Zielposition
Fülle die smoothScrollTo-Funktion mit der ersten Hälfte der Logik. Hier müssen wir die DOM-Abfrage für das scrollTargetID-Element und das menuElementID-Element durchführen. Danach berechnen wir die Zielposition für das Scrollen unter Berücksichtigung der Höhe des Menüs und des topOffset-Werts.
// smoothScrollTo.ts
export const smoothScrollTo = (scrollTargetID: string, menuElementID: string, topOffset: number) => {
// Query the DOM for the target and menu elements
const targetElement = document.querySelector(scrollTargetID);
const menuHeightElement = document.querySelector(menuElementID) as HTMLElement;
if (targetElement && menuHeightElement) {
// Get the location of the target element
const rect = targetElement.getBoundingClientRect();
// Calculate the target scroll position taking into account the menu's height and provided top offset
const targetPosition = (rect.top + window.scrollY - menuHeightElement.offsetHeight) === 0
? 0
: (rect.top + window.scrollY - menuHeightElement.offsetHeight - topOffset);
// The rest of the logic will be filled in the next steps...
}
};Schritt 4: Viewport-Höhe und maximale Scroll-Höhe berechnen
Die maximale Scroll-Länge maxScrollHeight ist die Distanz, die der Viewport durchscrollen muss, um ein Zielelement für den Benutzer sichtbar zu machen.
Ein Problem entsteht, wenn sich das Zielelement am Ende der Website befindet. In diesem Fall kann der Viewport nicht bis zur oberen Kante des Zielelements scrollen, da das Dokument bereits endet. Wird dies nicht berücksichtigt, führt es zu einer Animation, die abrupt stoppt, wenn die unterste Kante des Dokuments vom Viewport erreicht wird.
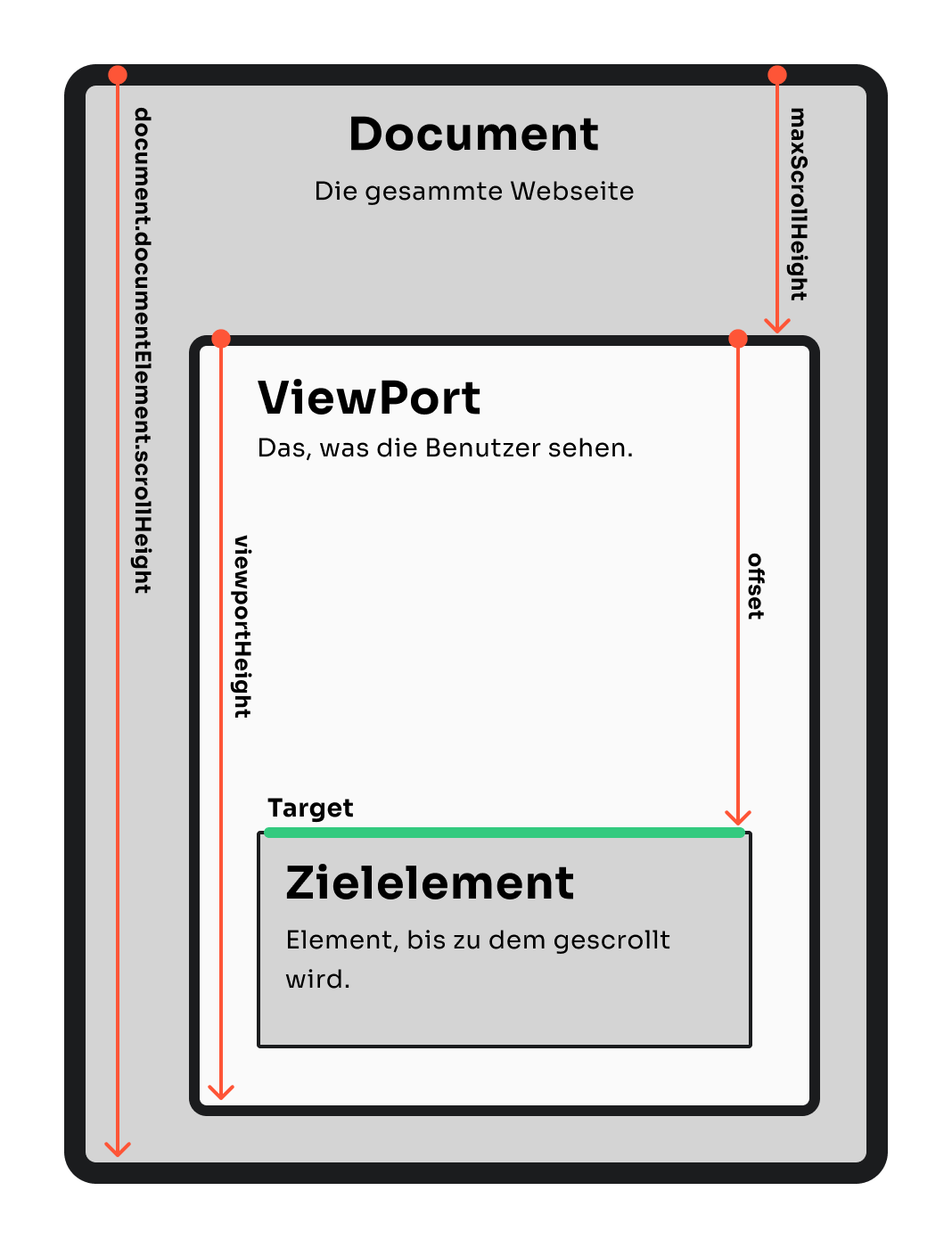
Um dies zu berücksichtigen, wird die maximale Scroll-Länge maxScrollHeight als die gesamte Scroll-Länge document.documentElement.scrollHeight minus der Höhe des Viewports window.innerHeight berechnet. Der Code dafür sieht wie folgt aus:
// smoothScrollTo.ts
export const smoothScrollTo = (scrollTargetID: string, menuElementID: string, topOffset: number) => {
// Query the DOM for the target and menu elements
const targetElement = document.querySelector(scrollTargetID);
const menuHeightElement = document.querySelector(menuElementID) as HTMLElement;
if (targetElement && menuHeightElement) {
// Get the location of the target element
const rect = targetElement.getBoundingClientRect();
// Calculate the target scroll position taking into account the menu's height and provided top offset
const targetPosition = (rect.top + window.scrollY - menuHeightElement.offsetHeight) === 0
? 0
: (rect.top + window.scrollY - menuHeightElement.offsetHeight - topOffset);
// Get the current scroll position
const currentPosition = window.scrollY;
// Get the viewport height
const viewportHeight = window.innerHeight;
// Calculate the maximum scrollable height
const maxScrollHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight - viewportHeight;
// The rest of the logic will be filled in the next steps...
}
};Schritt 5: Scroll-Distanz berechnen und Animation vorbereiten
Jetzt berechnen wir die Scroll-Distanz und bereiten die Animation vor, indem wir die Dauer und die kubische Ease-in-Out-Funktion festlegen.
// smoothScrollTo.ts
export const smoothScrollTo = (scrollTargetID: string, menuElementID: string, topOffset: number) => {
// Query the DOM for the target and menu elements
const targetElement = document.querySelector(scrollTargetID);
const menuHeightElement = document.querySelector(menuElementID) as HTMLElement;
if (targetElement && menuHeightElement) {
// Get the location of the target element
const rect = targetElement.getBoundingClientRect();
// Calculate the target scroll position taking into account the menu's height and provided top offset
const targetPosition = (rect.top + window.scrollY - menuHeightElement.offsetHeight) === 0
? 0
: (rect.top + window.scrollY - menuHeightElement.offsetHeight - topOffset);
// Get the current scroll position
const currentPosition = window.scrollY;
// Get the viewport height
const viewportHeight = window.innerHeight;
// Calculate the maximum scrollable height
const maxScrollHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight - viewportHeight;
let offset = 0;
// Adjust the target scroll position if it's below the maximum scrollable height
if (maxScrollHeight < targetPosition) {
offset = (targetPosition - maxScrollHeight);
}
const newTargetPosition = targetPosition - offset;
// Calculate the distance to scroll
const distance = newTargetPosition - currentPosition;
// Get the current time to calculate the animation duration later
const startTime = Date.now();
// Calculate the duration of the animation based on the scroll distance
const duration = Math.max(Math.abs(distance) / 3, 300);
// The rest of the logic will be filled in the next steps...
}
};Schritt 6: Kubische Ease-in-Out-Funktion implementieren und Animation durchführen
Implementiere die kubische Ease-in-Out-Funktion und führe die Animation aus, indem Du window.scroll in Kombination mit requestAnimationFrame verwendest.
// smoothScrollTo.ts
export const smoothScrollTo = (scrollTargetID: string, menuElementID: string, topOffset: number) => {
// Query the DOM for the target and menu elements
const targetElement = document.querySelector(scrollTargetID);
const menuHeightElement = document.querySelector(menuElementID) as HTMLElement;
if (targetElement && menuHeightElement) {
// Get the location of the target element
const rect = targetElement.getBoundingClientRect();
// Calculate the target scroll position taking into account the menu's height and provided top offset
const targetPosition = (rect.top + window.scrollY - menuHeightElement.offsetHeight) === 0
? 0
: (rect.top + window.scrollY - menuHeightElement.offsetHeight - topOffset);
// Get the current scroll position
const currentPosition = window.scrollY;
// Get the viewport height
const viewportHeight = window.innerHeight;
// Calculate the maximum scrollable height
const maxScrollHeight = document.documentElement.scrollHeight - viewportHeight;
let offset = 0;
// Adjust the target scroll position if it's below the maximum scrollable height
if (maxScrollHeight < targetPosition) {
offset = (targetPosition - maxScrollHeight);
}
const newTargetPosition = targetPosition - offset;
// Calculate the distance to scroll
const distance = newTargetPosition - currentPosition;
// Get the current time to calculate the animation duration later
const startTime = Date.now();
// Calculate the duration of the animation based on the scroll distance
const duration = Math.max(Math.abs(distance) / 3, 300);
// Define the cubic ease-in-out function
const easeInOutCubic = (t: number, b: number, c: number, d: number) => {
t /= d / 2;
if (t < 1) return c / 2 * t * t * t + b;
t -= 2;
return c / 2 * (t * t * t + 2) + b;
};
// Define the animation frame function
const animationFrame = () => {
const currentTime = Date.now();
// Calculate the time elapsed since the animation started
const time = Math.min(1, (currentTime - startTime) / duration);
// Calculate the new scroll position for this animation frame
const newPosition = easeInOutCubic(time, currentPosition, distance, 1);
// Scroll to the new position
window.scroll(0, Math.min(newPosition, maxScrollHeight));
// Continue the animation if we haven't reached the target position and the max scroll position yet
if (time < 1 && newPosition < maxScrollHeight) {
requestAnimationFrame(animationFrame);
}
};
// Start the animation
requestAnimationFrame(animationFrame);
}
};Schritt 7: Testen
Du hast die smoothScrollTo-Funktion erfolgreich erstellt! Du kannst jetzt die Funktion in Deiner Svelte-Anwendung verwenden, um sanfte Scroll-Effekte zu implementieren. Teste die Funktion, indem Du sie aufrufst und sieh, wie die Seite reibungslos zum angegebenen Element scrollt.
Herzlichen Glückwunsch! Du hast jetzt eine voll funktionsfähige smoothScrollTo-Funktion in Svelte und TypeScript erstellt, um Deine Webanwendung mit einer eleganten Scroll-Animation auszustatten.
Schritt 8: Importieren der Funktion in Deine Anwendung
Öffne die Hauptseite oder das Layout Deiner Svelte-Anwendung (normalerweise App.svelte) und importiere die smoothScrollTo-Funktion.
//App.svelte
<script lang="ts">
import { onMount } from 'svelte';
import { smoothScrollTo } from './smoothScrollTo';
</script>Schritt 9: Verwendung der onMount-Funktion
Verwende die onMount-Funktion von Svelte, um die smoothScrollTo-Funktion aufzurufen, sobald die Komponente geladen ist. Dies ermöglicht das automatische Scrollen, wenn die Seite geladen wird.
<script lang="ts">
import { onMount } from 'svelte';
import { smoothScrollTo } from './smoothScrollTo';
onMount(() => {
// Beispiel Verwendung: Scrolle zur 'content'-Sektion,
// berücksichtige die Höhe der 'navbar'
// und verschiebe die endgültige Position um 20 Pixel von der oberen Kante der 'content'-Sektion
smoothScrollTo('content', 'navbar', 20);
});
</script>Schritt 10: Ausprobieren
Speichere die Datei und starte die Svelte-Entwicklungs-Server mit dem folgenden Befehl:
npm run devÖffne Dein Webbrowser und navigiere zu Ihrer Svelte-Anwendung. Du solltest das sanfte Scrollen zur angegebenen scrollTargetID-Element sehen, während die Höhe des menuElementID-Elements und der topOffset-Wert berücksichtigt werden.
Herzlichen Glückwunsch! Du hast erfolgreich die smoothScrollTo-Funktion in Deinem Svelte-Projekt implementiert und kannst nun sanfte Scroll-Effekte in Deiner Webanwendung genießen.
Und falls Du weitere Fragen hast, buche gerne eine Website Beratung bei mir. Ich entwickle die Websites mit Svelte und integriere sie in WordPress zur Content-Verwaltung.
